SPECIES INFO
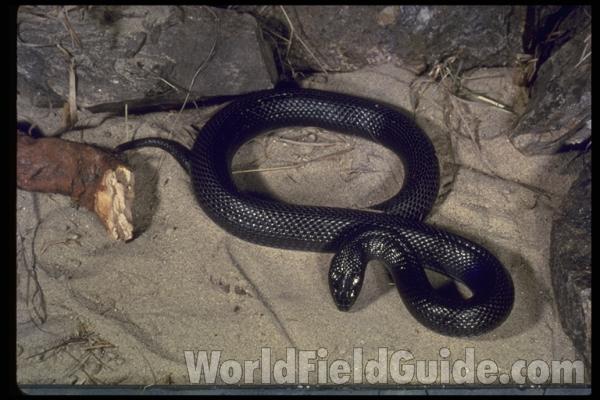
Desert black snake (Walterinnesia aegyptia) is found in the deserts of northern Africa and into the middle east. This snake is normally about three feet long. The bite from this species can be fatal.Desert black snake genus (Walterinnesia) contains one species of snake.
African Elapidae contain the Mambas (Genus Dendroaspis). These Mambas are among the most feared of all snakes. Some of the species in this genus reach giant sizes, climb trees, and are aggressive. Mambas frequently raise the front part of their body high before striking, and consequently hit the head and arms of humans with their deadly fangs. There are at least five distinct species of mambas. Mambas (Genus Dendroaspis) of Africa are among the most feared of all snakes.
Cobra and Coral Snake Group (Family Elapidae) is known for its deadly poisons. Some of the snakes in this group are small and not dangerous unless handled, stepped on, or disturbed. However, their venom is very deadly and they should all be considered potentially dangerous. There are almost 300 species in this family. The mambas, tiger snakes, and kraits also belong here. Australia has about 90 of these species.
Lizards and Snakes (Squamata Order) share many common characteristics and consequently they are grouped in a single order. There are greater differences between some groups of lizards than there are between other groups of lizards and snakes. The same is true of snakes. Lizards and snakes share a common skull shape.
There are perhaps 4,000 species of lizards and perhaps 2,700 species of snakes alive today. In the Great Big Book of Snakes and Reptiles published in 2014, they noted the above estimates.
Reptiles (Class Reptilia) are an ancient group of scaled chordates. These scales may be permanently joined, as in the turtles, or flexible, as in the snakes. Reptiles are land-based. Their eggs are laid on land and the young are air breathing.
In the Great Big Book of Snakes and Reptiles published in 2014, they noted that there are more than 7,000 species of reptiles alive today.
Backboned Animals (Phylum Chordata) are the most advanced group of animals on earth. These animals are characterized by having a spinal cord or backbone. Most members have a clearly defined brain that controls the organism through a spinal cord. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are in this phylum.
Currently, some taxonomists believe that the fish should be divided into two groups (sharks and regular fishes) and that there are some other primitive groups in the phylum such as hagfish or lampreys.
Animal Kingdom contains numerous organisms that feed on other animals or plants. Included in the animal kingdom are the lower marine invertebrates such as sponges and corals, the jointed legged animals such as insects and spiders, and the backboned animals such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.