SPECIES INFO
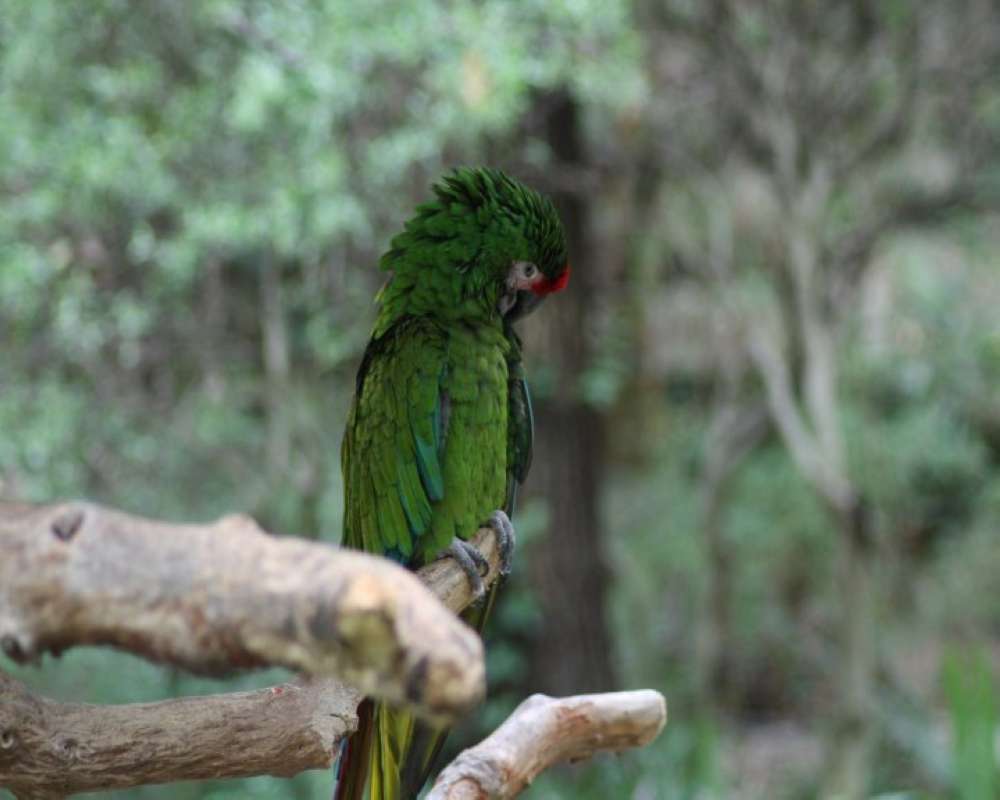
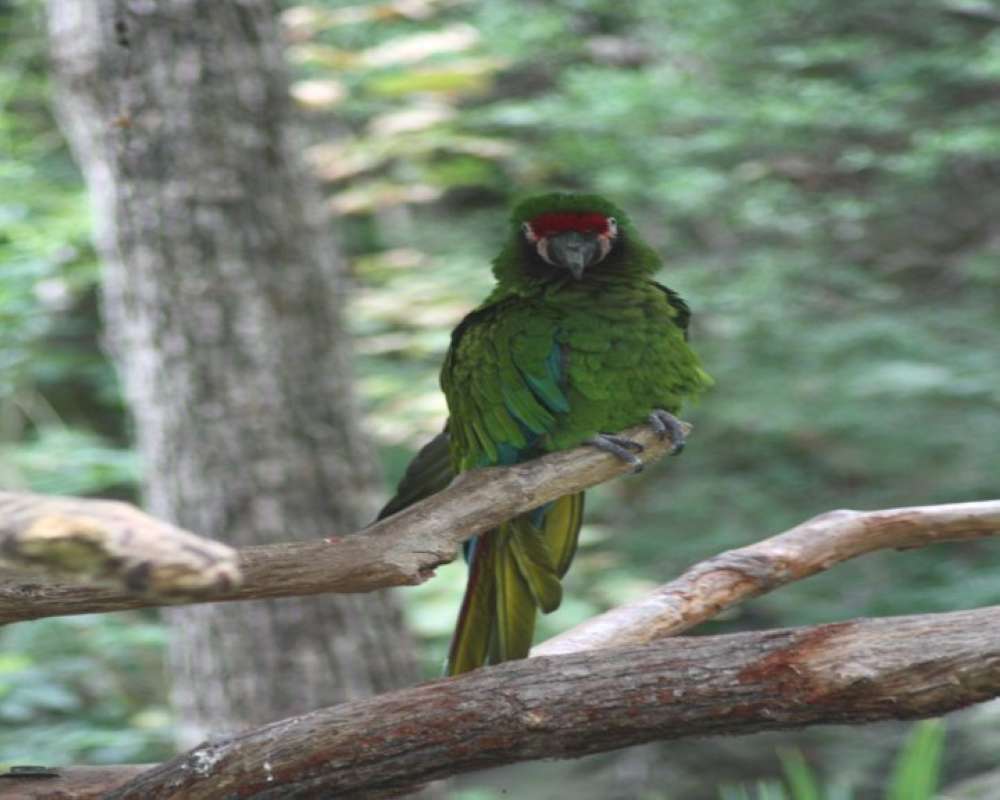
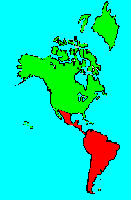
Military Green Macaw (Ara militaris) is found from Mexico to northern South America and then south to Bolivia. There are three subspecies. The Mexican form is found along the western coast of Mexico. The Mexican subspecies is from 27 to 30 inches long. When standing the Mexican form shows mostly green with a bit of blue on the wings. There is a small red patch above the bill. When flying the top of the tail shows red, and the dorsal side of the outer wing feathers show blue.
There are three formally described subspecies. The nominate subspecies, Ara militaris militaris, is found in northern Venezuela, western Colombia, eastern Ecuador, and south into northern Peru. The subspecies mexicanus is found in northern and central Mexico. The subspecies bolivianus is found from Bolivia east into northwestern Argentina.The Ara genus of macaws is native to the New World tropics. There are 15 species in this genus. Two of these are now extinct. The Cuban macaw and the Hispaniolan macaw are now gone. This leaves 13 species of these large and spectacular birds. We have entries for the remaining thirteen species. However, some modern taxonomists have removed 5 species from this genus and placed them into other genera including Orthopsittaca, Primolius, and Diopsittaca.
Of the remaining 8 species, 4 of them are either threatened or critically threatened with extinction.
We have arbitrarily separated the Macaws (Ara, Anodorhynchus, and Cyanopsitta) into a separate group. Although this is not a popular division, this helps one locate and study the New World tropical parrots and macaws.
Parrots (Family) is the single family in the Parrot order. This family has experienced quite a few fairly recent extinctions, including the Carolina Parakeet and several species that were previously found on the Caribbean Islands. The 128 species of parrots in the New World are particularly threatened.
Extensive rain forest clearing and bird capture for the pet trade remain important issues.
We have divided this very large family into groups to facilitate identification and study. We have used the Bates-Busenbark system that divides this family into 5 subfamilies. Owl parrots, Kea parrots, Lorikeets, Pigmy parrots, and the balance into the main family which includes the Macaws, Conures, Parrots, and Parakeets We have further divided the main sub family into three groups based on geography: New World, Eurasian to Australia, and African.
The following (incomplete and abbreviated) list of New World species are rare, threatened, endangered or extinct:
Threatened - Puerto Rican Amazon - Amazona vittata
Rare - Red spectacled Amazon - Amazona pretrei
Threatened - Red Tailed Amazon - Amazona brasiliensis
Rare - Red browed Amazon - Amazona rhodocorytha
Endangered - St. Lucia Amazon - Amazona versicolor
Endangered - Red Necked Amazon - Amazona arausiaca
Endangered - Imperial Amazon - Amazona imperialis
Endangered - St. Vincent Amazon - Amazona guildingi
Endangered - Indigo Macaw - Anodorhynchus leari
Endangered - Hyacinth Macaw - Anodorhy hyacinth
Extinct - Glaucus Macaw - Anodorhy glaucus
Extinct(?) - Blue Throat Macaw - Ara glaucogularis
Extinct - Cuban Red Macaw - Ara tricolor
Vulnerable - Golden Conura - Aratinga guarouba
Unknown - Rufous front Parakeet - Bolborhynch ferrugin
Extinct - Carolina Parakeet - Conurposis carolinensis
Endangered - Little Blue Macaw - Cyanopsitta spixii
Unknown - Rusty Faced Parrot - Hapalopsittaca amazonina
Threatened - Gold Plumed Conura - Leptositt branickii
Vulnerable - Yellow Ear Conura - Ognorhynchus icterotis
Rare - Blue Chest Parakeet - Pyrrhura cruentata
Rare - Brown Backed Parrotlet - Touit melanonota
Unknown - Golden tailed Parrotlet - Touit surda
Parrots (Order Psittaciformes) are an order of over 330 species of birds that are found in the warmer parts of the world. (Craig Robinson in his book of SE Asian birds estimates worldwide parrot species at about 358 species.) Many of the species are brightly colored. Characteristics of this order include a top bill which hooks downward, and two toes pointing forward and two toes pointing to the rear. Most students place all the species in this order in a single family.
Many of the species in this family are desirable cage birds, which adds to their vulnerability in their native habitat. For example, a captured Hyacinth Macaw may sell for over $20,000 retail. While most of the species are protected, the various laws seem to have little effect on the trade. However, captive breeding may help protect them.
Aves contains about 8,650 different species of living birds known to science. Each year about one new species is discovered in some remote rain forest or remote island. In addition, scientists have been raising many subspecies to full species status which may raise the species count to 10,000. Birdlife recognizes 10,027 species as of 2011.
However, each year about one species goes extinct. The rate of extinction is increasing, and the rate of new discovery is decreasing, so that the number of bird species will soon begin to decline rapidly. Although different taxonomists would organize the birds differently, there are approximately twenty-seven orders of birds. These orders are broken down into about one hundred and fifty-five different families.
Recent research of the genetic structure of some of the shore birds and owls would indicate that the present organization of orders and families should have some modification.
The birds are a worldwide group of animals that are characterized by having the front limbs modified into wings that are used for flying. Perhaps the most unique feature of the birds is the feathers. These feathers are made up of a central support called a quill and a series of small filaments that are hooked together as barbs.
For many years it was believed that Archaeopteryx discovered in Bavaria was the oldest bird from about 150 million years ago. However, in l986, Sankar Chattterjee, a Texas paleontologist, reportedly discovered a bird in the genus Protoavis that lived about 225 million years ago.
When this project was begun in 1978, we used Austin & Singer for bird taxonomy. Since then, we have adopted many changes, but have kept some older concepts that are still found widely in the literature. Recently, we have used Clements and Howard & Moore. Very recently, we have used Monroe and Sibley for the higher taxonomy of the perching birds.
Backboned Animals (Phylum Chordata) are the most advanced group of animals on earth. These animals are characterized by having a spinal cord or backbone. Most members have a clearly defined brain that controls the organism through a spinal cord. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are in this phylum.
Currently, some taxonomists believe that the fish should be divided into two groups (sharks and regular fishes) and that there are some other primitive groups in the phylum such as hagfish or lampreys.
Animal Kingdom contains numerous organisms that feed on other animals or plants. Included in the animal kingdom are the lower marine invertebrates such as sponges and corals, the jointed legged animals such as insects and spiders, and the backboned animals such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.