SPECIES INFO
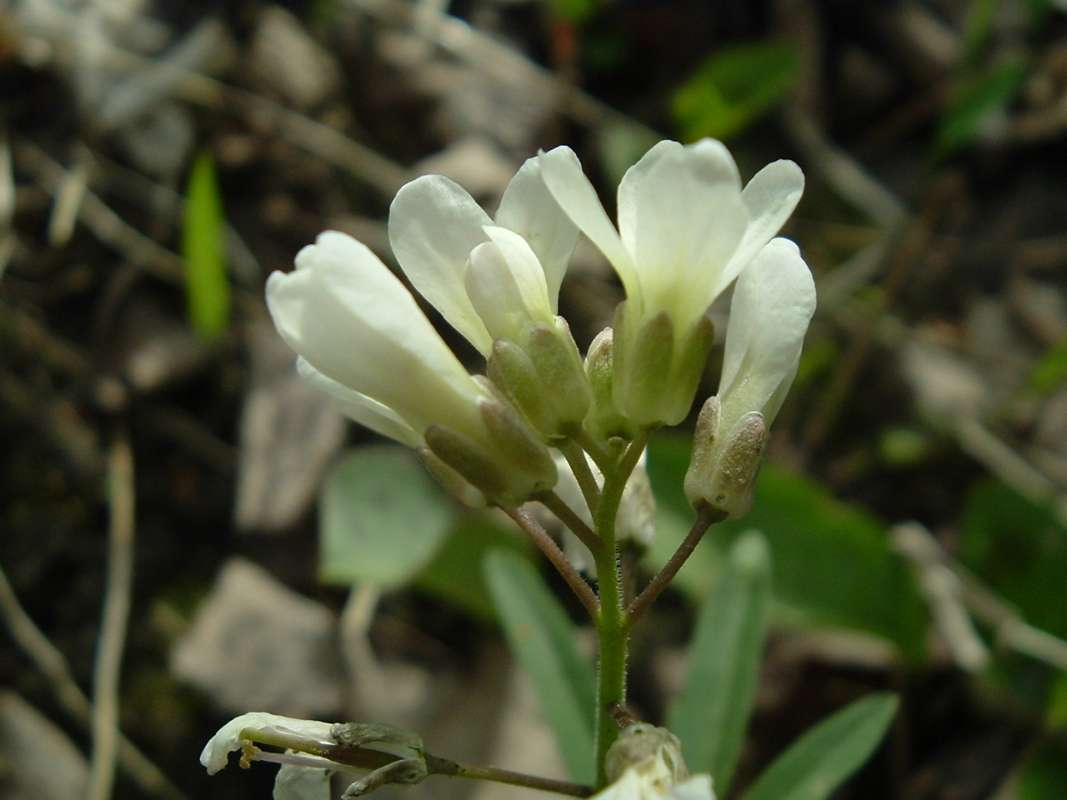
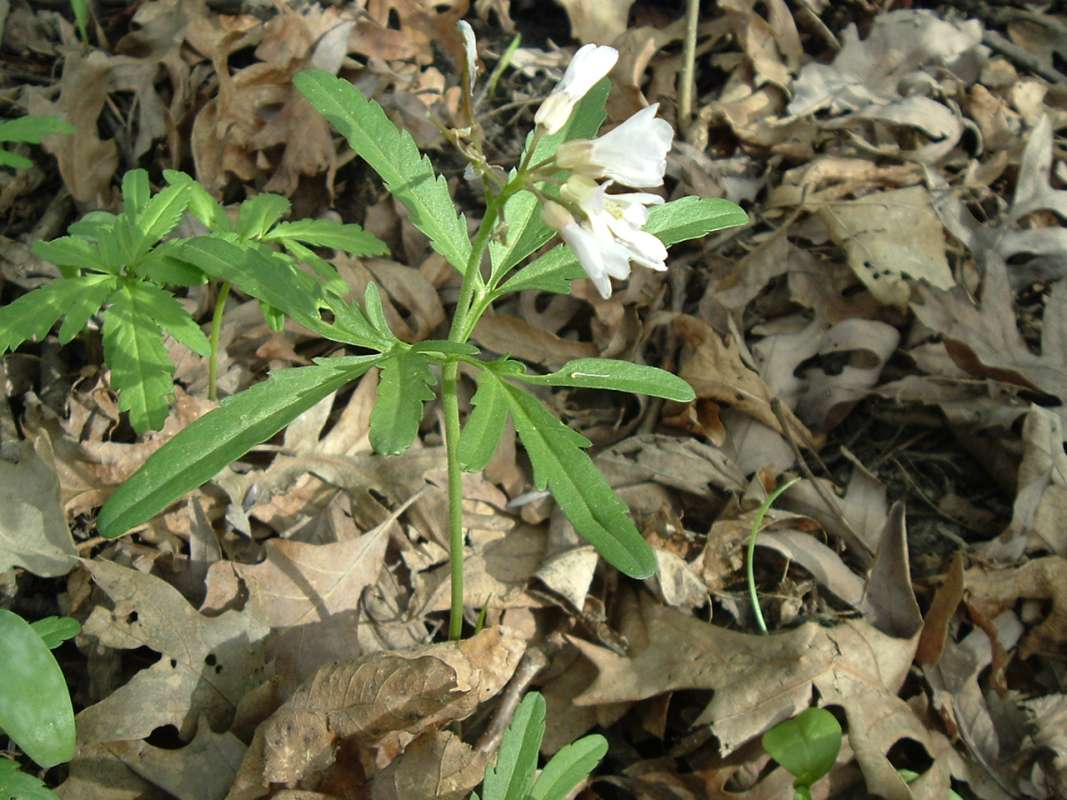
Cut-leaved toothwort (Dentaria laciniata to Cardamine laciniata to Cardamine concatenata)is found from Quebec west to Minnesota and south to Florida, Louisiana, and Kansas. This plant prefers moist or rich woods. This perennial herb is less than 15 inches tall. The frequently whorled three part leaves are petioled. The divisions are themselves frequently toothed or lobed. The flowers are white or pink or rose colored.Dentaria genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. However, most of the species in this genus have been moved to the Cardamine genus.
Mustard Family (Cruciferae to Brassicaceae) is found naturally worldwide with the exception of the dry areas south of the Amazon. This family is also absent from the dry areas of south eastern Africa. This is a very large family of mostly herbs. There are about 2,800 to 3,500 species usually organized into about 340 to 400 different genera. Modern botanists would like to change the name of this family to the Brassicaceae family. There are about 700 species arranged into about 100 genera growing in greater North America.
The members of this family or mostly annual or perennial herbs, with a few subshrubs. The leaves are alternate and simple. Flowers usually have four petals.
The family is important for food including brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, kale, kimchi, radishes, mustard, and turnips. The family contains several weeds that are particularly troublesome to farmers in the genera Brassica and Barbarea. Hesperis, wallflower, and cresses are found in gardens.
Rhoeadales Order includes the Poppies, Mustards, and mostly other non-woody groups of plants.
Dicots (Dicotyledoneae Class) are the predominant group of vascular plants on earth. With the exception of the grasses (Monocots) and the Conifers (Gymnosperms), most of the larger plants that one encounters are Dicots. Dicots are characterized by having a seed with two outer shell coverings.
Some of the more primitive Dicots are the typical hardwood trees (oaks, birches, hickories, etc). The more advanced Dicots include many of the Composite (Aster) Family flowers like the Dandelion, Aster, Thistles, and Sunflowers. Although many Monocots reach a very high degree of specialization, most botanists feel that the Dicots represent the most advanced group of plants.
Seed plants (Phylum Embryophyta) are generally grouped into one large phylum containing three major classes: the Gymnosperms, the Monocots, and the Dicots. (Some scientists separate the Gymnosperms into a separate phylum and refer to the remaining plants as flowering plants or Angiospermae.)
For North American counts of the number of species in each genus and family, the primary reference has been John T. Kartesz, author of A Synonymized Checklist of the Vascular Flora of the United States, Canada, and Greenland (1994). The geographical scope of his lists include, as part of greater North America, Hawaii, Alaska, Greenland, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands.
Kartesz lists 21,757 species of vascular plants comprising the ferns, gymnosperms and flowering plants as being found in greater North America (including Alaska, Hawaii, Greenland, Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands.
There are estimates within the scientific world that about half of the listed North American seed plants were originally native with the balance being comprised of Eurasian and tropical plants that have become established.
Plant kingdom contains a large variety of different organisms including mosses, ferns, and seed plants. Most plants manufacture their energy from sunlight and water. Identification of many species is difficult in that most individual plants have characteristics that have variables based on soil moisture, soil chemistry, and sunlight.
Because of the difficulty in learning and identifying different plant groups, specialists have emerged that study only a limited group of plants. These specialists revise the taxonomy and give us detailed descriptions and ranges of the various species. Their results are published in technical journals and written with highly specialized words that apply to a specific group.
On the other hand, there are the nature publishers. These people and companies undertake the challenging task of trying to provide easy to use pictures and descriptions to identify those species.