SPECIES INFO
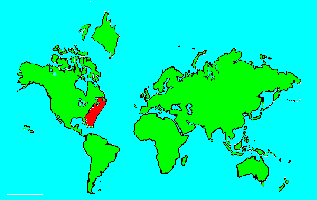
Grasby (Epinephelus cruentatus) is found in the western Atlantic from Florida, the Bahamas, and the Gulf of Mexico south to southern Brazil. This small grouper is normally less than 12 inches in length. This is a brownish green species with some white a(sometimes dark) spots below the dorsal fins.In marine waters of eastern North America and the Bahamas, the members of this fish genus are called groupers. However, near Australia, the name of cod or rock cod is frequently used. (For the Australian species, we have changed the common name in some instances from cod to rockcod.) Many of these are commercially hunted for their valuable meat. These are frequently solitary reef dwelling fish that prey on other fish. Some of the members of this genus can become quite large. There are about 40 species in this genus.
The true groupers subfamily (Epinephelinae) contains six to eight genera and about 40 species. The genera include: Aethaloperca, Cephalopholis, Dermatolepis, Epinephelus, Mycteroperca, Paranthias, and Stereolepsis. Many large species are included in this subfamily. Most species hide in caves under coral, and when an unsuspecting fish swims into range, they lunge forward and gray their prey.
Sea Bass and grouper family (Serranidae) is found worldwide in marine waters and several kinds inhabit freshwater. There are about 450 species distributed among about 50 genera in this family. They are considered good sport fish. Many are important food fish. Several species can be poisonous. Some individuals grow to tremendous sizes. The first dorsal fin is usually heavily spined, and the frequently seemingly joined second dorsal fin is soft spined. Some species change sex as they get older, and other species can have both sexes at the same time.
This family is frequently broken down into several different subfamilies including:
Epinephelinae with six-eight genera and about 40 species. The genera include: Aethaloperca, Cephalopholis, Dermatolepis, Epinephelus, Mycteroperca, Paranthias, and Stereolepsis.
Grammistinae including the genera Diploprion, Grammistes, Rainfordia, and Rypticus.
Serraninae including the genera Diplectrum, Hypoplectrus, Centropristis, and Serranus.
Anthiinae including the genera Anthias, Caesioperca, Callanthias, Caprodon, Ellerkeldia, Epinephelides, Lepidoperca, Orthos, Plectranthis, Sacura, Selenanthias.
Pseudochrominae including the genera Labracinus, Pseudochromis, and Pseudoplesiops.
Plesiopidae including the genera Calloplesiops, Plesiops, and Trachinops.
(We have used the Burgess-Axelrod check list at the back of their book 9 on Pacific marine fishes, as a starting point. We have made some additional adjustments.)
Perch-like Fish, Order Perciformes, are the largest order of fish in both freshwater and shallow saltwater. Most of the conventional fish belong to this order. The bass, bluegills, perch and crappies of freshwater plus the groupers and sea bass of salt water belong to this order. The fish all have spiny rays in their fins and the tail fin has seventeen rays. There are approximately 150 families. Herein, we have placed the families in alphabetical sequence within this order. (In some instances the typical taxonomic sequence of families is not much help. Consider, for example, that the barracudas are usually placed between the mullets and the threadfins.)
Bony fish, Class Teleostomi, are a class of chordates that include the majority of fish-like animals found on earth. They are characterized by a bony jaw and a bony skeleton. They are found in both fresh and marine waters.
Backboned Animals (Phylum Chordata) are the most advanced group of animals on earth. These animals are characterized by having a spinal cord or backbone. Most members have a clearly defined brain that controls the organism through a spinal cord. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are in this phylum.
Currently, some taxonomists believe that the fish should be divided into two groups (sharks and regular fishes) and that there are some other primitive groups in the phylum such as hagfish or lampreys.
Animal Kingdom contains numerous organisms that feed on other animals or plants. Included in the animal kingdom are the lower marine invertebrates such as sponges and corals, the jointed legged animals such as insects and spiders, and the backboned animals such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.